





| PM2.5 (µg/m³) | PM10 (µg/m³) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | 24hrs | Annual | 24hrs | |
| Indian (CPCB) | 40 | 60 | 60 | 100 |
| USA (US EPA) | 15 | 65 | 50 | 150 |
| Europe (UK EPA) | - | - | 30 | 50 |
| WHO | 10 | 25 | 20 | 50 |
Most studies show that PM2.5 levels of 12 µg/m3 or below are deemed healthy, with little to no danger from exposure. But, if the quantity reaches or exceeds 35 µg/m3 in 24 hours, the air is classified as hazardous. Hence, it might create problems for persons who already have breathing problems, such as asthma. Moreover, prolonged exposure to levels exceeding 50 µg/m3 can result in major health problems and untimely death.
Particulates are smaller, microscopic particles invisible to the naked eye. Thus, PM1 and PM2.5 can enter your bloodstream via respiration. Further, Short-term and long-term exposure to PM has a variety of health effects including various cardiorespiratory diseases. Hence, short-term impacts include irritation in the eyes, nose, and throat. And long-term impacts are permanent respiratory problems such as asthma and bronchitis, heart diseases, and heart failure.
Irritation in the eyes
Irritation in the nose
Irritation in the throat
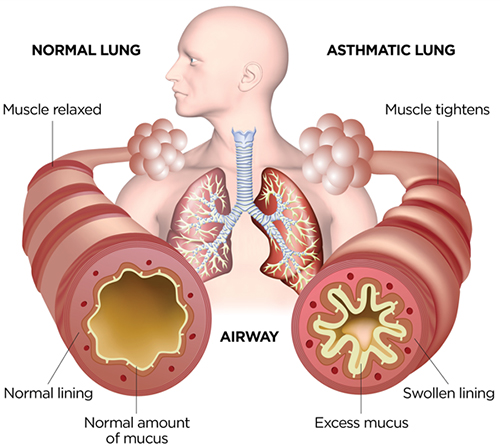
Asthma Problem
Heart diseases and Heart failure
Without a doubt, YES! Even in small amounts, particulate can make you feel uneasy or sick.
The ability of a particle to evade the body's defences and enter the lungs deeply increases with particle size. But, people with respiratory and heart conditions, children, and the elderly may be more vulnerable to PM2.5. Furthermore, Long-term exposure to fine particulate matter may also be associated with increased cases of chronic bronchitis, impaired lung function, and an increase in mortality rates from cardiorespiratory disease, according to research.